Databases
One of the most powerful and unique features of SlashDB is the ability to automatically discover tables, views and relations in databases.
In this section we're going to connect SlashDB to a sample database and make it usable to user admin. The procedure is fairly simple and will take just a moment.
Database Definitions list
The Database Definitions page provides a list of all data sources available for viewing and interaction. It can be searched using search field above the list or sorted by clicking on headers of the columns.
The list is accessible from the main Menu Configure > Databass or direct URL /dbdef. It is available only admin and users with Administrative privilege to view list of Databases.
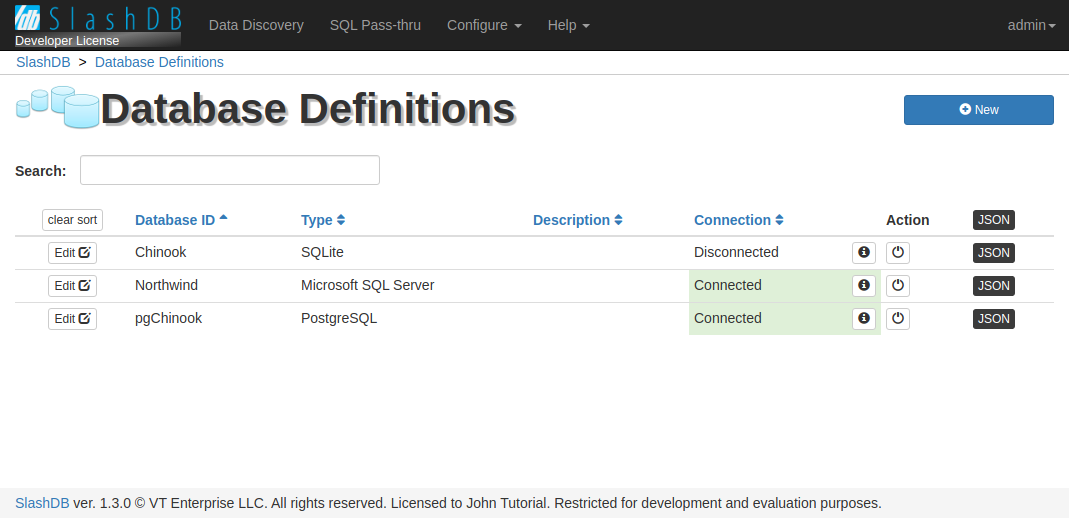
The list can be searched using search field above the list or sorted by clicking on headers of the columns.
On the list you can find  button to edit database details, Database ID, Type, Description, Connection status,
button to edit database details, Database ID, Type, Description, Connection status,  button that toggles the state of the selected database and link to JSON representation.
button that toggles the state of the selected database and link to JSON representation.
Adding a new database
1. Click on Configure > Databases in menu to show list of database definitions
2. Next click the  in top right corner.
The button is visible for admin and users with
Administrative Privilege
to create new database.
in top right corner.
The button is visible for admin and users with
Administrative Privilege
to create new database.
3. The modal with configuration wizard will appear.
Start by choosing database type you wish to connect by clicking on database logo.
At this point out of the box SlashDB can connect to: MS SQL Server, ORACLE, IBM DB2, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite and SQLCipher.

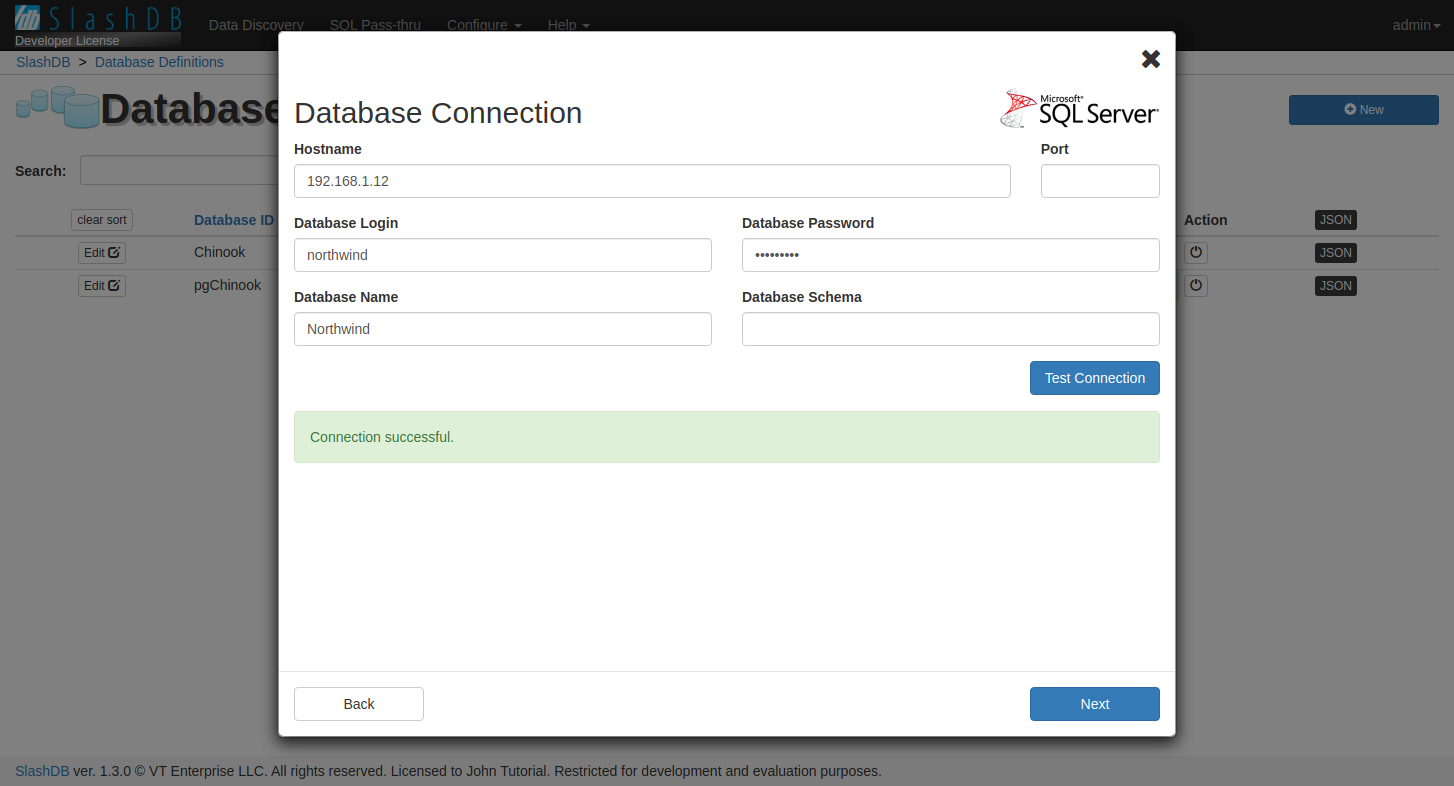
Next, fill in the connection details for the database. Note that depending on selected database type the list of fields may be different than pictured.
Click "Test Connection" to verify that the database server is reachable. If it fails we recommend to resolve connection problems before proceeding.
You can ignore the connection problem for now and finish adding new database. Later you can adjust the connection details by editing database configuration.
Click "Next" to proceed.
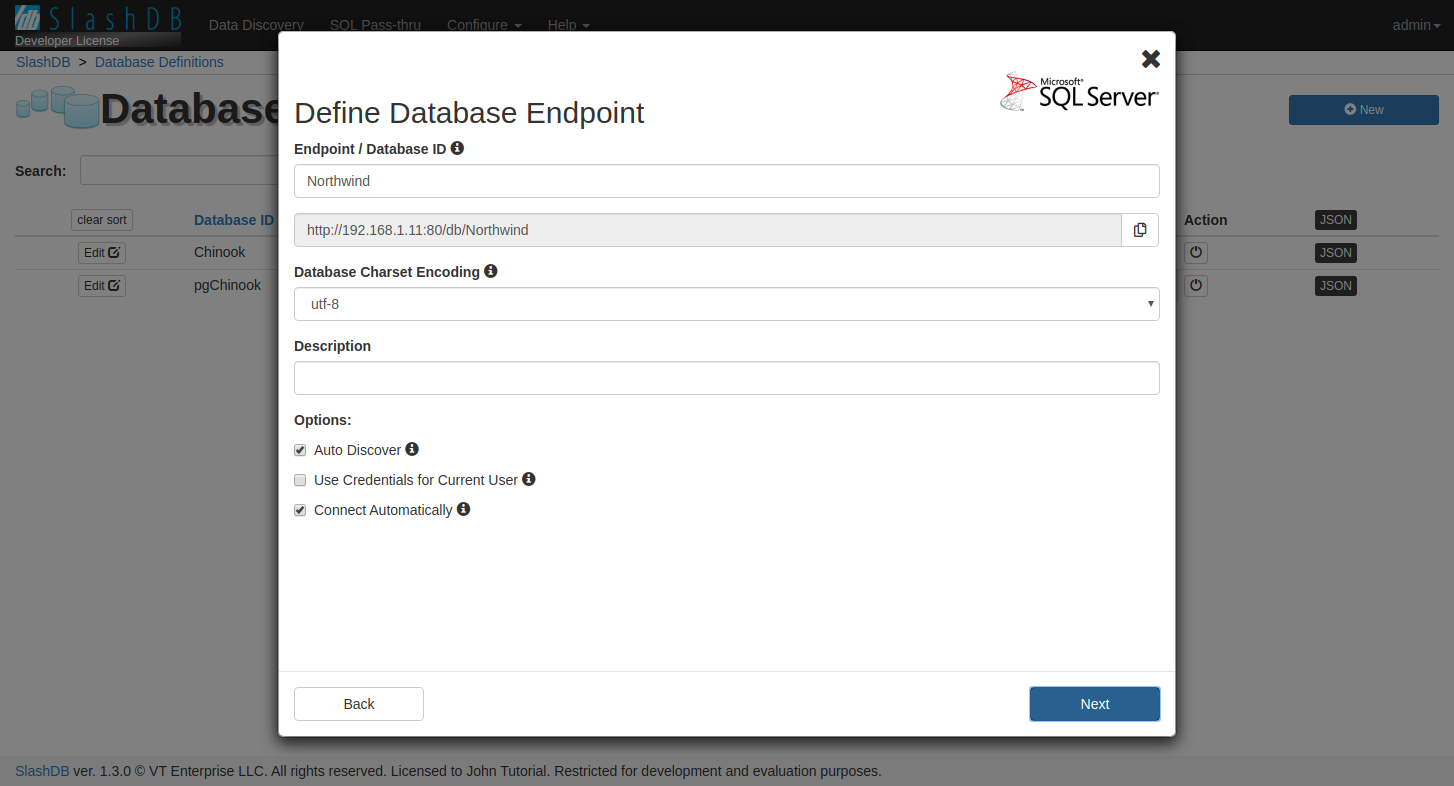
Fill the details for the API that will be created.
Hover your mouse cursor over the  icon to learn more about the
purpose of the field and configuration tips.
icon to learn more about the
purpose of the field and configuration tips.
- Choose a name for your database in SlashDB. This will become the Endpoint in Data Discovery and Database ID in SQL Pass-thru.
- Pick charset encoding used on your database server.
- Optionally add a description.
By default SlashDB will be discovering all available tables in you database and will do that automatically whenever system starts.
Keep in mind that database credentials you provided in previous step are used only for the process of discovering tables. After adding the database you should modify SlashDB user settings and add a database mapping. See user configuration section Database Mapping.
Clicking "Next" will save your new database configuration and start connecting to the database.
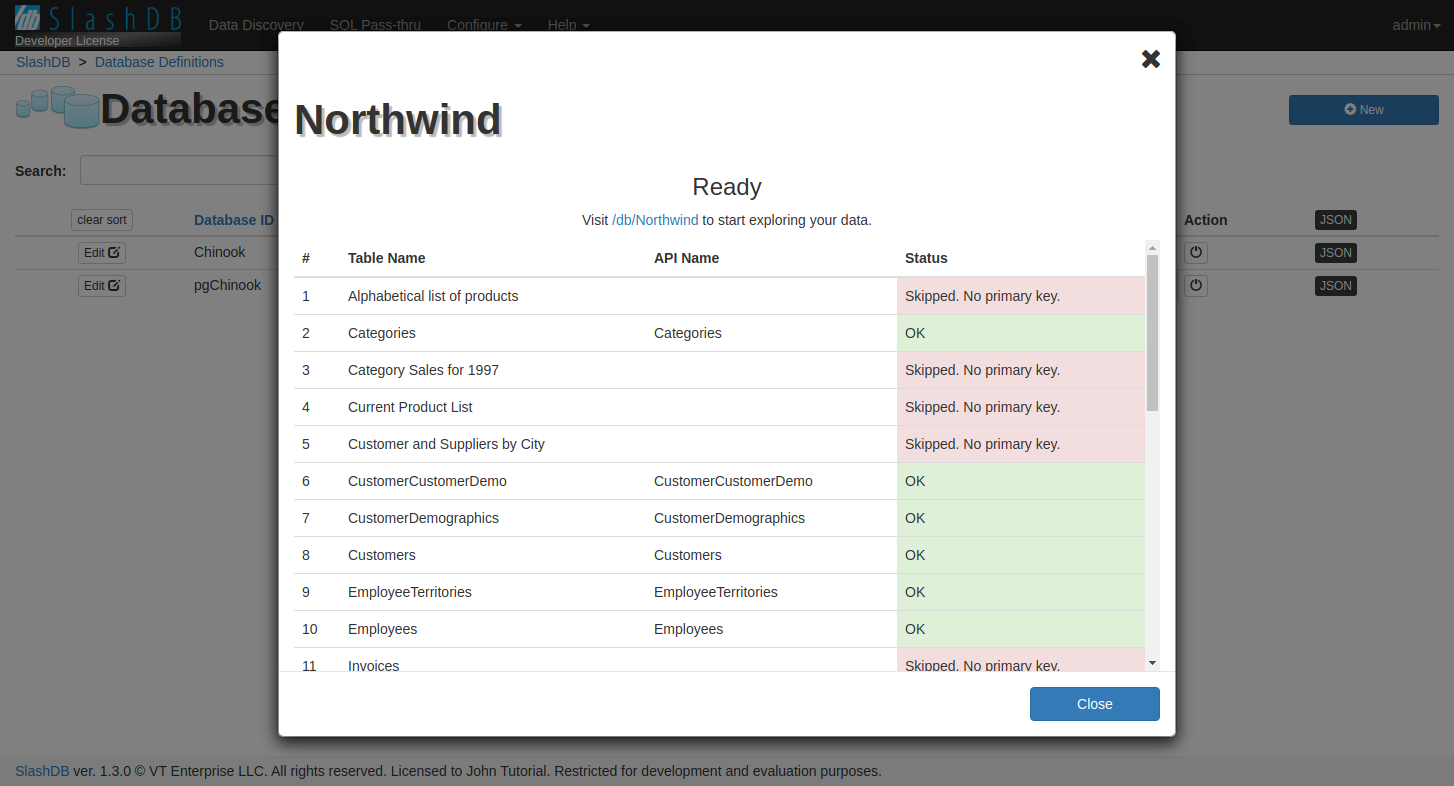
For small databases the tables are reflected immediately. If there ara many large tables in the database you will see a progress bar on the screen and reflection status for each created API.
When process is completed you will see a screen like below with a message "Ready". It means you can start exploring your data.
3. In the Database ID field give the database a unique name and optionally put a short description in the Description field.
4. Select appropriate database type from the Type drop-down menu and fill out the remaining fields on the screen. Hover your mouse cursor over the  icon to learn more about the purpose of the field and configuration tips.
icon to learn more about the purpose of the field and configuration tips.
Note that depending on the database type selected the list of fields may be different than pictured.
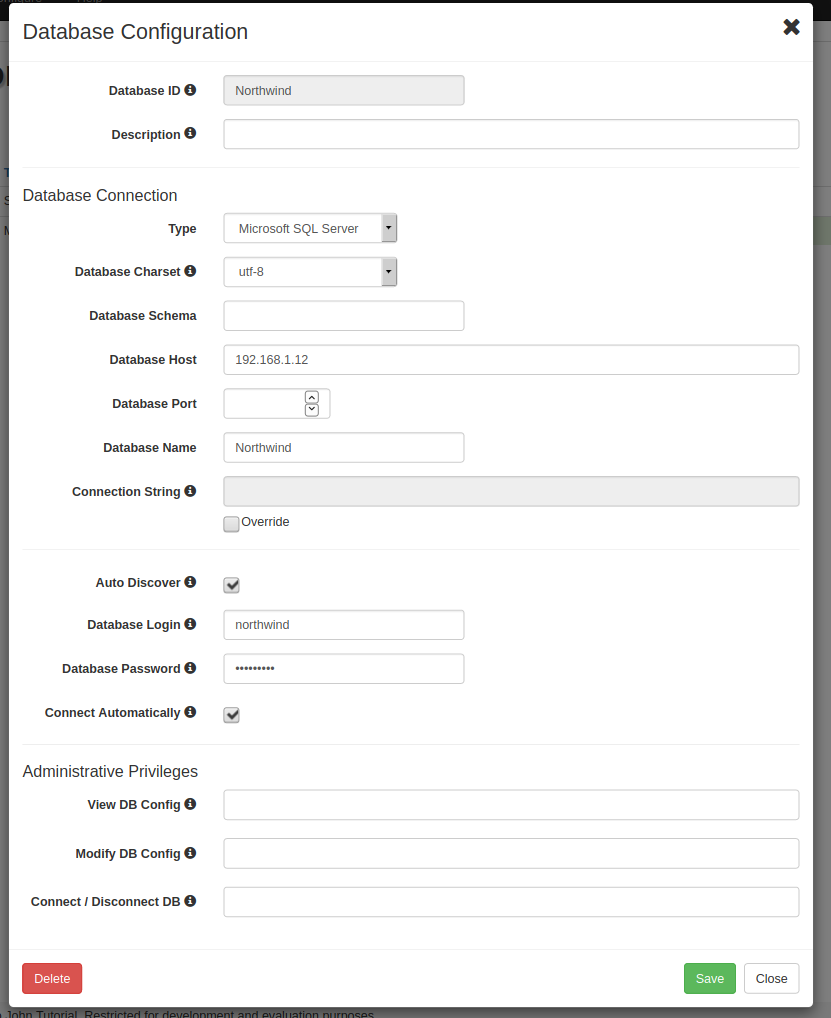
5. When finished click the Save button. If Use Credentials for Current User is selected then on saving another modal will popup showing updated user configuration with mapping to the database defined using Database User and Database Password. Save and close and then Close the configuration of the database.
Now the newly added database will appear in the Database Definitions table.
Connect to database
Use  on Data Discovery
on Data Discovery /db or Database Definitions /dbdef page to change the Connection status of the database.
Failed Connection
When something goes wrong while connecting to a datbase, SlashDB will change the Connection status to Failed. If necessary, it will also display a notification bellow the databases list, with more information about the problem.
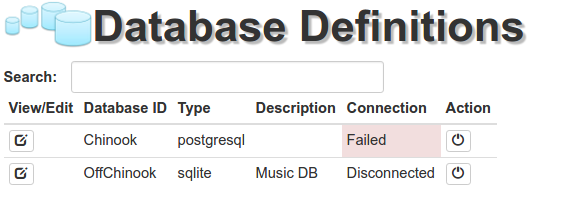
A failed connection usually occurs because of the following two reasons:
- an error in the database configuration - please check the database definition for typos/errors,
- network errors due to a firewall blocking access to the database or network down time - check the firewall and grant access from the SlashDB host to the host and port on which the database server is running.
You may need to ask your database and/or network administrator for help.
Configuration File
Database configurations are stored in YAML file /etc/slashdb/databases.cfg.
A simple configuration for single SQLite database called Chinook looks like below
Chinook:
alternate_key: {}
autoload: true
autoload_user: {dbpass: '', dbuser: ''}
connection: /var/lib/slashdb/sqlite/chinook.sqlite
creator: admin
db_encoding: utf-8
db_id: Chinook
db_schema: null
db_type: sqlite
desc: Example SQLite database
excluded_columns: {}
execute: []
foreign_keys: {}
autoconnect: true
read: []
write: []
It's easier to modify database configuration using Configuration GUI. Some features are hidden and require modifying databases.cfg manually.
Database Configuration Attributes
The file stores all database configurations in dictionary like structure. The keys of the highest level are unique database ids. Each database configuration has several attributes. Below you can find all attributes explained and some examples.
alternate_key
Data Discovery reflects only tables with primary keys. When a primary key is not defined it may be manually added to config under in alternate_key dictionary.
Since database views typically don't have primary key, this feature allows to them to SlashDB.
The alternate_key is a dictionary. The keys in the dictionary are names of tables, values are lists of column names that can be treated as artificial primary key.
Example:
Chinook:
alternate_key:
Table1: [col1, col2]
ViewCustomer: [CustomerId]
autoload
When true tells SlashDB to make a full reflect on database. This will discover tables, columns, primary and foreign keys and automatically add them to the API.
When false SlashDB will be looking for the model installed as plugin with the same name. This feature is used for advanced use cases with custom built ORM model.
Example:
SlashDB will automatically discover database model
Chinook:
autoload: true
SlashDB will be looking for a custom model installed as a plugin.
Chinook:
autoload: false
autoload_user
It's a dictionary that stores login and password to the database to be used for reflect purposes. It must be used together with autoload = true
Example:
Chinook:
autoload: true
autoload_user: {dbuser: 'john', dbpass: 'secretpasssowrd'}
connection
Connection stores location of the database.
For SQLite it's path to file e.g. /home/john/database.sqlite.
For MS SQL, DB2, MySQL, MariDB, PostgreSQL it's host, port and database e.g. 192.168.1.1:1433/Chinook.
For Oracle it's host, port and SID e.g. 192.168.1.1:1521/xe
Example
Chinook:
connection: database.my-domain:1433/Chinook
creator
Creator options is used for administrative purposes. User which adds a new database config is assigned as a creator and is automatically granted permissions to read, modify and connect the database.
Example
User admin has added the database to SlashDB.
Chinook:
creator: admin
db_encoding
This option tells SlashDB what is the charset encoding in the database. This information in required to correctly process diacritic characters. Allowed values are:
| utf-16-be | utf-16-le | utf-7 | utf-8 | ascii |
| big5 | big5hkscs | cp037 | cp424 | cp437 |
| cp500 | cp737 | cp775 | cp850 | cp852 |
| cp855 | cp856 | cp857 | cp860 | cp861 |
| cp862 | cp863 | cp864 | cp865 | cp866 |
| cp869 | cp874 | cp875 | cp932 | cp949 |
| cp950 | cp1006 | cp1026 | cp1140 | cp1250 |
| cp1251 | cp1252 | cp1253 | cp1254 | cp1255 |
| cp1256 | cp1257 | cp1258 | ujis | eucjis2004 |
| eucjisx0213 | euckr | gb2312 | gbk | gb18030-2000 |
| hz-gb-2312 | iso-2022-jp | iso-2022-jp-1 | iso-2022-jp-2 | iso-2022-jp-2004 |
| iso-2022-jp-3 | iso-2022-jp-ext | iso-2022-kr | iso-8859-1 | iso-8859-2 |
| iso-8859-3 | iso-8859-4 | iso-8859-5 | iso-8859-6 | iso-8859-7 |
| iso-8859-8 | iso-8859-9 | iso-8859-10 | iso-8859-13 | iso-8859-14 |
| iso-8859-15 | cp1361 | koi8_r | koi8_u | mac_cyrillic |
| mac_greek | mac_iceland | mac_latin2 | mac_roman | mac_turkish |
| ptcp154 | shiftjis | shiftjis2004 | shiftjisx0213 | utf-16 |
Example:
The character set used by database is UTF-8.
Chinook:
db_encoding: 'utf-8'
db_id
Unique database id that is used in other configuration files: users.cfg and querydefs.cfg. Also the id becomes an API endpoint in Data Discovery e.g. /db/Chinook.
Example:
Chinook:
db_id: Chinook
db_schema
This option is used if SlashDB should connect to certain schema in the database. That's applicable for databases that support use schema like MS SQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, DB2. If not provided a default user schema is used.
Example:
Use database schema dbo when reflecting model.
Chinook:
db_schema: dbo
db_type
Defines what sort of a database server SlashDB is connecting.
Allowed values are:
sqlitefor SQLitemssqlfor MS SQL Serveroraclefor Oracledb2for IBM DB2mysqlfor MySQL or MariaDBpostgresqlfor PostgreSQL
Example:
The database Chinook is SQLite
Chinook:
db_type: sqlite
desc
Non-obligatory additional description of the purpose of the API or any other useful notes.
Example:
Chinook:
desc: A sample music store database
excluded_columns
This option allows to exclude certain columns from the API but columns cannot be part on relationship constraint.
When primary key column is excluded the table won't be added to the API. This can be used as a feature to hide some tables.
Option excluded_columns expects a dictionary object where key is table name and value is list of column names to be excluded form API.
Example:
To exclude a regular columns Company, Address and City from table Customer and BillingAddress from table Invoice
Chinook:
excluded_columns:
Customer: [Company, Address, City]
Invoice: [BillingAddress]
To exclude a table from API exclude the primary key.
Chinook:
excluded_columns:
InvoiceLine: [InvoiceLineId]
foreign_keys
Deprecated. Should be empty dictionary or null.
Chinook:
foreign_keys: null
autoconnect
This option accept true or false value that define if the API should connect automatically to the server when SlashDB starts.
Example:
To load (reflect) Chinook database automatically on start of the service.
Chinook:
autoconnect: true
read
List of users allow to view the database config. Account admin is always privileged and doesn't have to listed.
Example:
Only john, mike and admin will be able view the config details.
Chinook:
read: [john, mike]
write
List of users allowed to modify the database config.Account admin is always privileged and doesn't have to listed.
Example:
Only john, mike and admin will be able view the config details.
Chinook:
read: [john, mike]
execute
It's a list of SlashDB users allowed to control state of that particular API - connect or disconnect. Account admin is always privileged and doesn't have to listed.
Example:
Only john, mike and admin will be able change the state of the connection.
Chinook:
execute: [john, mike]