SQL Pass-thru
SQL Pass-thru enables users to execute custom defined queries. This screen is different from SQL Pass-thru configuration in that it is accessible to all users and only query execution is possible.
Queries list
The Queries screen provides a list of executable queries. The list is accessible from the main Menu SQL Pass-thru or with direct URL /query.
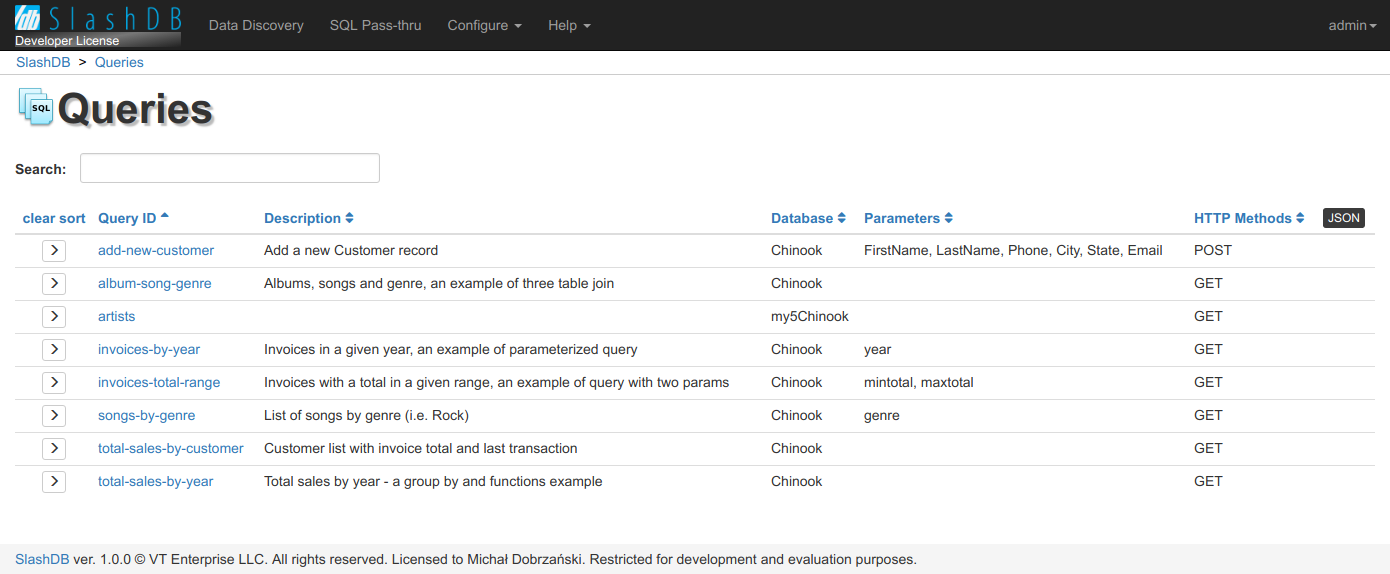
Listed are queries to which currently logged in user has execute permission. User "admin" has always access to all queries.
The list can be searched by Query ID, Description and Database using search field above the list or sorted by clicking on headers of the columns.
To Run certain query click on  or Query ID.
or Query ID.
Query ID is a unique identifier for the query which is used when making HTTP requests. For example:
- /query/songs-by-genre/genre/Rock.json - execute the query with parameter genre: Rock
- /querystudio/songs-by-genre - open the query definition in Query Studio
The list contains also some Description of the query, the Database in which the query will execute, Parameters required by the query, allowed HTTP Methods.
The  button in the top right corner of the table is a link to the list of executable queries in JSON format.
button in the top right corner of the table is a link to the list of executable queries in JSON format.
Executing Query
GUI
When certain query is selected from the list a view for edit/execute is opened.
Users with execute and view/edit permission on the query will see full Query Studio editor with execute form in lower part of the window.

Users with only execute permission will see different layout that doesn't allow to view details of the query.
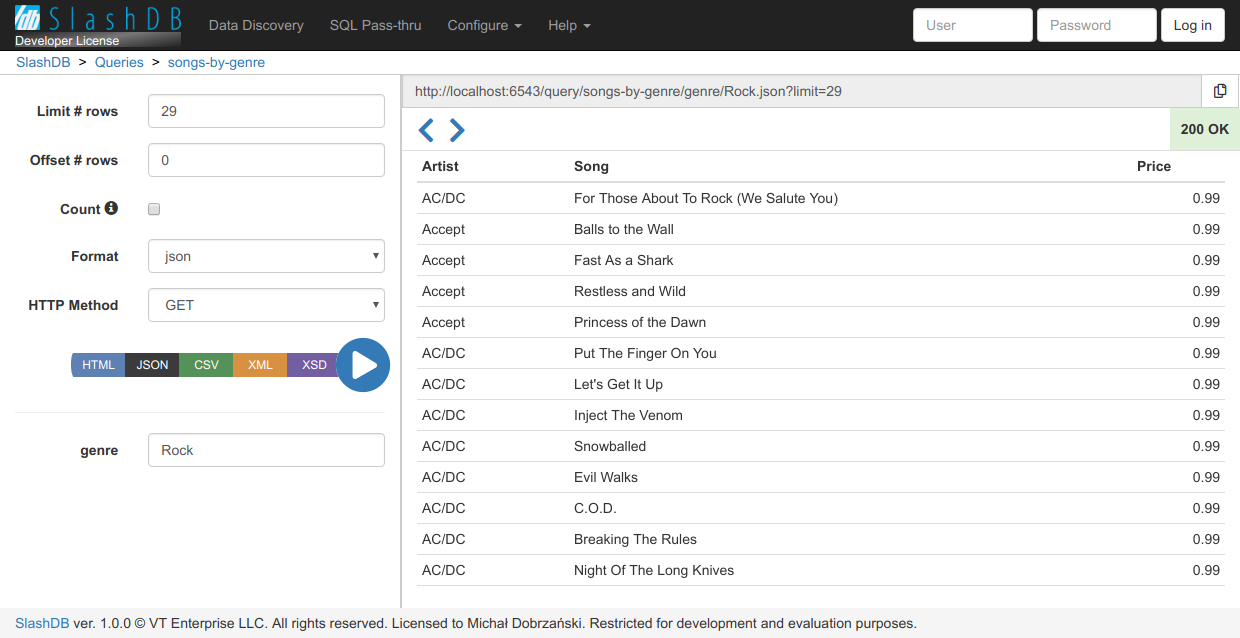
To execute the query fill the parameters, then
- click on round play button to see output in results panel,
- click on buttons for specific format that slide out when hovering over play button,
- press
enterwhen focused on parameter form to see output in results panel.
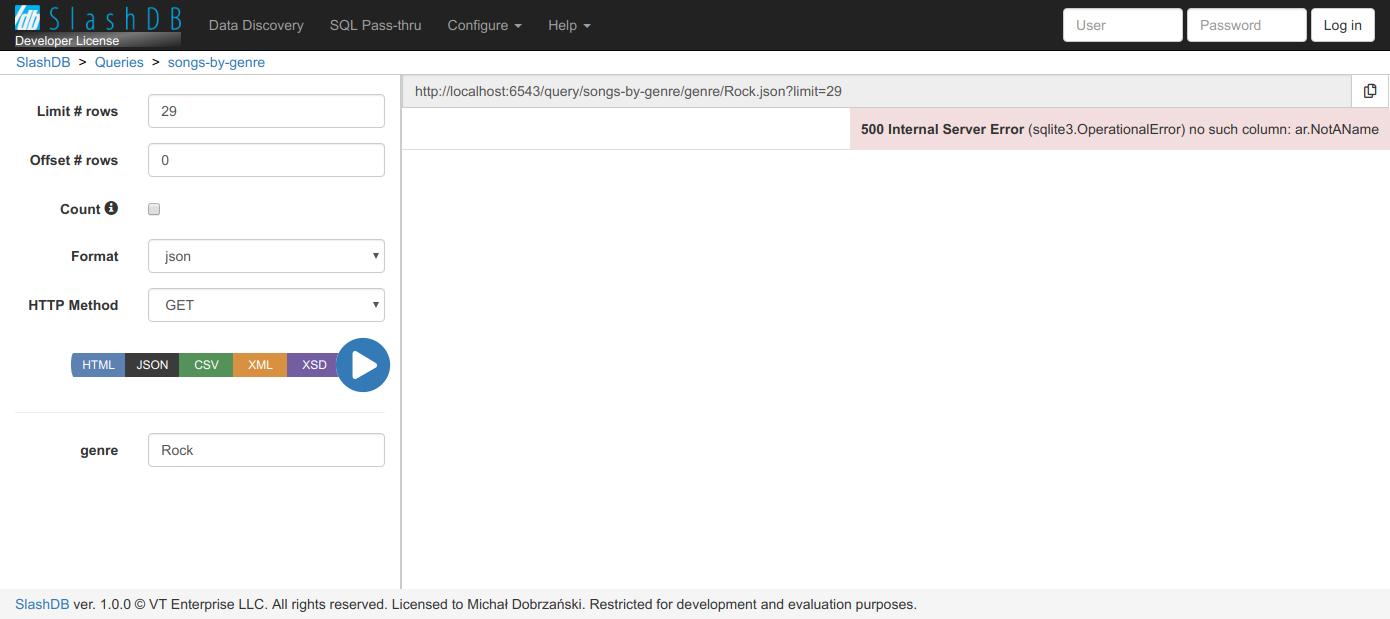
Errors
Any problems executing the statement like SQL syntax error are shown in Results tab of the GUI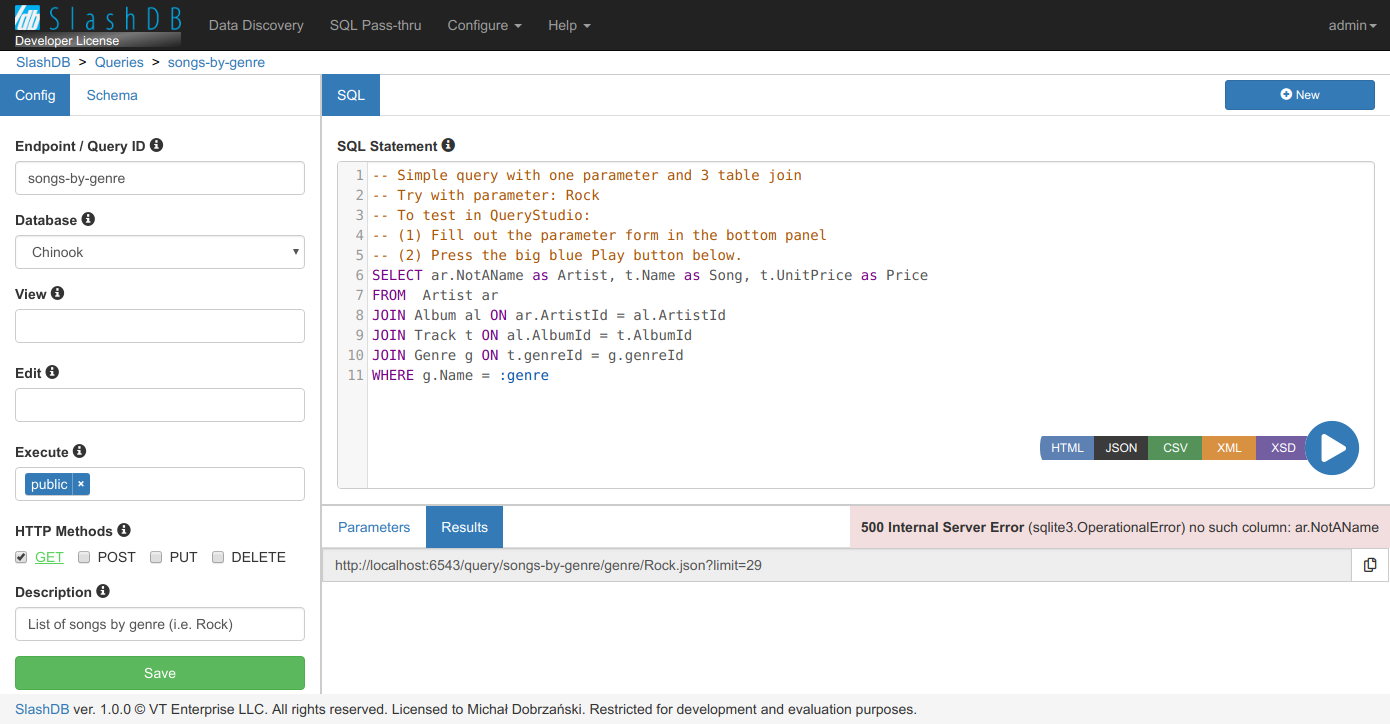
REST
Each SQL Pass-thru query has its own endpoint to run it with HTTP request. Right HTTP method must be used on the URL constructed of query id, parameters and output format. All that information is available either on list of queries or query definition.
GET or DELETE
For HTTP methods GET or DELETE parameters can be send only in URL segments.
Examples:
GET request to SlashDB Demo server on query customer-in-city with single query parameter city eqal Paris.
curl -X GET "https://demo.slashdb.com/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.json"
GET request to SlashDB Demo server on query without any parameters - sales-by-year.
curl -X GET "https://demo.slashdb.com/query/sales-by-year.json"
PUT or POST
For HTTP methods PUT or POST parameters can be send either in URL segments or in body in data format matching the request format (json, xml, csv).
POST with parameters passed in URL
curl -X POST "https://demo.slashdb.com/query/add-new-customer/FirstName/John/LastName/Tutorial/Phone/123 456 789/City/New York/State/NY/Email/john.tutorial@slashdb.com.json"
Bulk execute
Multiple parameter sets can be passed in body of PUT or POST request which results in executing the query multiple times, each time with different parameters. All SQL statements are executed in single transaction and changes are rolled back if any error happens.
Usage:
Body in CSV
ParamName1,ParamName2
Param Value 1, Param Value 2
Param Value 3, Param Value 4
Body in JSON
[
{
"ParamName1": "Param Value 1",
"ParamName2": "Param Value 2"
},
{
"ParamName1": "Param Value 1",
"ParamName2": "Param Value 2"
}
]
Body in XML
For XML parameter sets must be wrapped in tags parameters and param_set.
<parameters>
<param_set>
<ParamName1>Param Value 1</ParamName1>
<ParamName2>Param Value 2</ParamName2>
...
</param_set>
<param_set>
<ParamName1>Param Value 11</ParamName1>
<ParamName2>Param Value 22</ParamName2>
</param_set>
...
</parameters>
If needed the tags can be changed in INI settings
xml_sdb.sqlpassthru_params.root_tag = parameters
xml_sdb.sqlpassthru_params.set_tag = param_set
Examples:
POST request with two parameter sets in JSON body
curl -X POST "https://demo.slashdb.com:443/query/add-new-customer.json" \
-d @- << EOF
[
{
"FirstName":"John",
"LastName":"Tutorial",
"Phone":"123 456 789",
"City":"New York",
"State":"NY",
"Email":"john.tutorial@slashdb.com"
},
{
"FirstName":"Monica",
"LastName":"Tutorial",
"Phone":"123 456 789",
"City":"New York",
"State":"NY",
"Email":"monica.tutorial@slashdb.com"
}
]
EOF
POST request with two parameter sets in XML body
curl -v -X POST "https://demo.slashdb.com/query/add-new-customer.xml" \
-d @- << EOF
<parameters>
<param_set>
<FirstName>John</FirstName>
<LastName>Tutorial</LastName>
<Phone>123 456 789</Phone>
<City>New York</City>
<State>NY</State>
<Email>john.tutorial@slashdb.com</Email>
</param_set>
<param_set>
<FirstName>Monica</FirstName>
<LastName>Tutorial</LastName>
<Phone>222 222 222</Phone>
<City>New York</City>
<State>NY</State>
<Email>john.tutorial@slashdb.com</Email>
</param_set>
</parameters>
EOF
Errors
When execution of the query fails the explanation will be returned in the header warning and response body in format matching to the request.
Examples:
Header "warning"
warning: (sqlite3.OperationalError) no such column: ar.NotAName
JSON error output
{
"url_template": "/query/songs-by-genre/genre/{genre}.json",
"http_code": 500,
"description": "(sqlite3.OperationalError) no such column: ar.NotAName"
}
CSV error output
url_template,http_code,description
/query/songs-by-genre/genre/{genre}.csv,500,(sqlite3.OperationalError) no such column: ar.NotAName
XML error output
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<SDBTest>
<http_code>500</http_code>
<description>(sqlite3.OperationalError) no such column: ar.NotAName</description>
<url_template>/query/songs-by-genre/genre/{genre}.xml</url_template>
</SDBTest>
Query Result
Result rows can be presented in XML (with XSD), JSON and CSV.
Examples:
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.json - SQL Pass-Thru query result in JSON.
In cases when you need only certain columns from your query result you can add a segment to the URL with comma separated names of columns.
Usage:
/query/[query_id]/[columnA],[columnB],[columnC]
Value Type: comma separated list of valid column names
Examples:
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris/FirstName,LastName.json - the output will contain only columns FirstName and LastName (State and Phone were excluded).
Options
url string substitution
This feature allows to replace part of the url with string defined in query parameter.
Visit this documentation page for detailed explanation.
sort
This feature allows to sort the output of query. The original SQL statement is wrapped in additional SQL for efficient sorting in database. Visit this documentation page for detailed explanation.
distinct
This feature allows to remove duplicate rows of the output. The original SQL statement is wrapped in additional SQL for efficient distinct filtering in database. Visit this documentation page for detailed explanation.
limit and offset
This feature allows to limit and skip rows of returned data. Visit this documentation page for detailed explanation.
transpose
This feature transposes output by converting column to rows and rows to columns. Visit this documentation page on transpose for detailed explanation.
count
When using this query string argument in request the response will contain also additional header SlashDB-All-Record-Count that tells what's the total count of rows returned by the query. Useful when using limit and offset with.
Usage:
?count
Response Header:
SlashDB-All-Record-Count:2
Value type: (no value)
Default: (not used)
Examples:
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.json?count - response contains header with total number of rows returned by query (header SlashDB-All-Record-Count: 2)
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.json?count&limit=1 - like above example but with additional limit=1, header SlashDB-All-Record-Count still is 2, even though we're using limit.
$ curl -v 'https://demo.slashdb.com/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.json?count&limit=1'
* Hostname was NOT found in DNS cache
* Trying 50.19.250.51...
* Connected to demo.slashdb.com (50.19.250.51) port 443 (#0)
[...]
> GET /query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.json?count&limit=1 HTTP/1.1
> User-Agent: curl/7.35.0
> Host: demo.slashdb.com
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
* Server nginx/1.4.6 (Ubuntu) is not blacklisted
< Server: nginx/1.4.6 (Ubuntu)
< Date: Thu, 12 Jul 2018 15:00:22 GMT
< Content-Type: application/json
< Content-Length: 139
< Connection: keep-alive
< SlashDB-All-Record-Count: 2
<
[
{
"LastName": "Bernard",
"State": null,
"FirstName": "Camille",
"Phone": "+33 01 49 70 65 65"
}
]
Options (XML)
nil visible
This feature allows to force showing empty tags.
Usage:
?nil_visible=[True_or_False]
Value type: boolean (True or False)
Default: False
Examples:
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.xml - not showing empty tags by default
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.xml?nil_visible=False - not showing empty tags
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.xml?nil_visible=True - showint empty tags
xmlType
This feature allows to adjust XML output.
Usage:
?xmlType=[name_of_xml_type]
Value type: string
Value options:
- adPersistXML - MS XML Persistance Format contains schema and Recordsets in single document
Default: (not used)
Examples:
/query/customers-in-city/city/Paris.xml?xmlType=adPersistXML - rendering XML in Persistance Format.