Users
Administrators manage SlashDB users by accessing the User Definitions screen from the main menu Configure > Users.
Typically APIs require some level of authentication and authorization. SlashDB comes with a robust security mechanism, which allows to create individual accounts with varying level of access. It supports authentication with a username and password or with an API key.
Let's watch how an admin creates a new user account for john.tutorial:
At first, the newly created account does not have access to any data. Later the admin adds a mapping between SlashDB account john.tutorial and an actual database login. From then on, john.tutorial's requests will run against the database using database login "chinook", under the permissions as configured for that user in the database server.
User Definitions list
The User Definitions page provides a list all of users/accounts already setup in SlashDB.
The list is accessible from the main Menu Configure > Users or direct URL /userdef. It is available only admin and users with Administrative privilege to view list of Users.
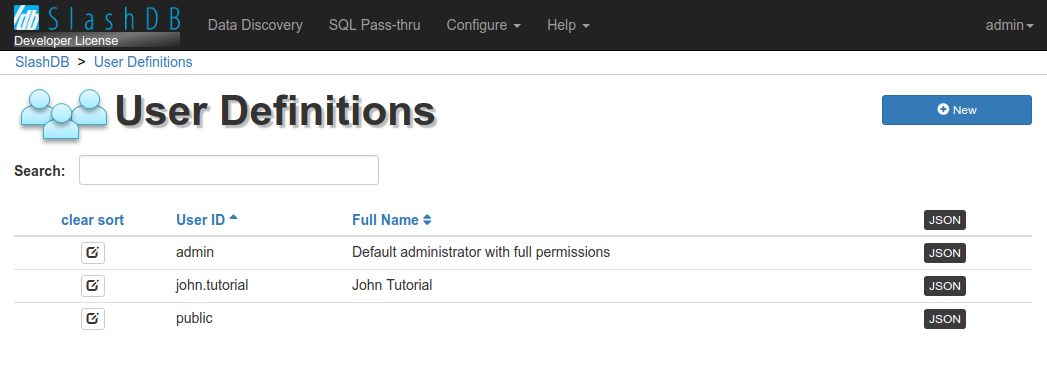
It can be searched using search field above the list or sorted by clicking on headers of the columns.
On the list you can find  button to edit user details, User ID, Full Name and link to JSON representation.
button to edit user details, User ID, Full Name and link to JSON representation.
Special accounts
admin - this is an account with administrative privileges and access to all system features. However, it does not have automatic authorization to data, which has to be configured with a database mapping.
public - acts like a regular account, but does not require any authentication. Just like a regular account it has to be configured with the mapping to access data.
Adding a new user
1. Click on Configure > Users in menu to show list of users
2. Next click on the  button. It is visible to admin and users with Administrative Privilege to create new users.
button. It is visible to admin and users with Administrative Privilege to create new users.
3. The modal of empty User Confguration will appear. Hover your mouse cursor over the  icon to learn more about the field's purpose and configuration tips.
icon to learn more about the field's purpose and configuration tips.
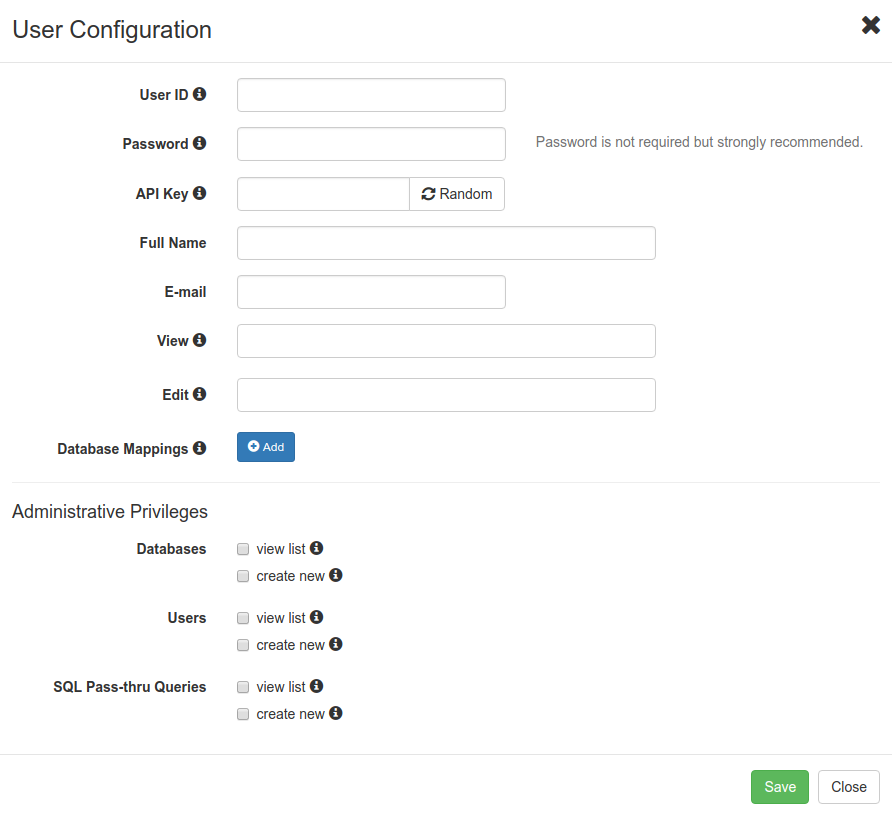
Basic information
Fill out the User ID field to give the account a unique name, also it's worth to set Full Name, E-mail for better describing the account.
Authentication & Authorization
Set Password for the account to be used in GUI and Basic Authentication.
The API Key identifies the user, so it has to be unique. The Random button generates a random sequence of characters for the API Key but it also can be set manually. The API key is a preferred way to authenticate into SlashDB programmatically. If API key is not set then this method of authentication is disabled for that user.
View is a list of users that should be allowed to see details of this user configuration and Edit is list of users allowed to modify it.
To give a user permissions to a databases, click the  button to configure Database Mappings. Select a Database ID from the drop-down list, then enter login and password for that database. These are actual database server credentials under which this SlashDB user will be operating.
If a database doesn't require or does not support logins (such as SQLite databases), add the mapping but leave the db user and db password fields blank.
button to configure Database Mappings. Select a Database ID from the drop-down list, then enter login and password for that database. These are actual database server credentials under which this SlashDB user will be operating.
If a database doesn't require or does not support logins (such as SQLite databases), add the mapping but leave the db user and db password fields blank.
To find out more on security in SlashDB see this section.
Administrative privileges
This section determines if user is available to view configuration lists of Database Definitions, User Definitions, Query Definitions or if he's allowed to add new databases, users or queries.
For regular users and applications leave those unchecked. For power users and secondary admins select the appropriate permissions.
User Configuration of account admin does not show this part because admin has unlimited access.
Configuration File
User configurations are saved in the YAML file /etc/slashdb/users.cfg.
Below you can find a simple configuration for users admin, public and app1 and details about each option.
admin:
api_key: 61527b29:5a031433fff9ff3edbcbc9f13f7b7026
creator: admin
databases:
Chinook: {dbpass: '', dbuser: ''}
dbdef: []
edit: [admin]
email: ''
name: Default administrator with full permissions
password: $6$rounds=697243$8B7YGw6fOYSQw.2O$iQvj/Z3SP5ob647xTRidfRpGvCfzB6S1DaPvnYQZZggWWyAcZ6.0ld/zOe9SzF18he4OtjKgL8EyvsWboew9t/
querydef: []
userdef: []
view: []
user_id: admin
public:
api_key: null
creator: admin
databases:
dbdef: []
edit: [admin]
email: ''
name: ''
password: ''
querydef: []
userdef: []
view: []
user_id: public
app1:
api_key: app1api:oqjbz59qca8ba0df
creator: admin
databases:
Chinook: {dbpass: '', dbuser: ''}
dbdef: []
edit: [admin]
email: app1-contact@mycompany.com
name: User with access to Chinook database
password: $6$rounds=656000$MLzjH30FKz22DCxO$nslVMsK4jbj5EeCCfz/Xd2gHiG2tCjeqWo3p8USCG9j6TvfX6H7dRvjJ9N7gGGzoUBY6oGrihFjWULk./Gm1I.
querydef: []
userdef: []
view: []
user_id: mike
It's easier to modify user configuration using GUI. Some features are hidden in GUI and require modifying users.cfg manually.
Each user configuration is defined under it's username e.g. app1 and contains several options.
User Configuration Attributes
The file keeps all configurations in dictionary like structure. The keys of the highest level are unique user ids. Each user configuration has several attributes. Below you can find all attributes explained and some examples.
api_key
This option keeps information for API Key authentication. See section Security/Authentication/API Key.
Example:
Request that is sent with App Id "app1api" and Api Key "oqjbz59qca8ba0df" in header or query string will be executed on behalf of user app1.
app1:
api_key: app1api:oqjbz59qca8ba0df
creator
This option keeps information about user that has created this account.
Example:
SlashDB account app1 was created by admin.
app1:
creator: admin
databases
This option keeps information about access granted to certain databases and credentials used when connecting the database. It's a dictionary structure where key is name of database defined in SlashDB and value is a dictionary with database login under dbuser and database password under dbpass keys.
Example:
SlashDB account app1 was given access to:
- SQLiteChinook (SQLite) database that doesn't require database user and password since it's SQLite,
- MSNorthwind (MS SQL) database and app1 will be using database login
northwind_roand passwordsome-passwordto run queries on the database.
app1:
databases:
SQLiteChinook: {dbpass: '', dbuser: ''}
MSNorthwind: {dbpass: 'some-password', dbuser: 'northwind_ro'}
user_id
Unique user id. Must be the same as the main key in the users.cfg file.
name
User's full name or more detailed description for the account.
Example:
app1:
name: Account used by Application-1 to acquire data
password
Hashed password. The password can be modified only by admin or the user himself.
The only way to reset admin's password is by setting empty password for admin manually in users.cfg file, restart service and visit GUI where user will be able to set new password for admin.
Example:
Hashed password for user app1
app1:
password: $6$rounds=656000$MLzjH30FKz22DCxO$nslVMsK4jbj5EeCCfz/Xd2gHiG2tCjeqWo3p8USCG9j6TvfX6H7dRvjJ9N7gGGzoUBY6oGrihFjWULk./Gm1I.
Empty password for user admin to set new password in GUI.
admin:
password: ''
User's email for contact and identification purposes.
Example:
app1:
email: app1-contact@mycompany.com
dbdef
Permissions to view list of database configs or add new one to SlashDB.
Accepted keywords:
- view
- create
Example:
User app1 granted to view list and create new database config.
app1:
dbdef: [view, create]
User app2 granted only to view list of database configs.
app1:
dbdef: [view]
querydef
Permissions to view list of query configs or add new one to SlashDB.
Accepted keywords:
- view
- create
Example:
User app1 granted to view list and create new query config.
app1:
querydef: [view, create]
User app2 granted only to view list of query configs.
app1:
querydef: [view]
userdef
Permissions to view list of user configs or add new one to SlashDB.
Accepted keywords:
- view
- create
Example:
User app1 granted to view list and create new user config.
app1:
userdef: [view, create]
User app2 granted only to view list of user configs.
app1:
userdef: [view]
view
List of users allowed to view this user config. User admin doesn't have to be added to the list because he's granted full access to all configs anyway.
Example:
Only admin and mike are allowed to view config of account app1.
app1:
view: [mike]
edit: [admin]
List of users allowed to change this user config. User admin doesn't have to be added to the list because he's granted full access to all configs anyway.
Example:
Only admin and mike are allowed to change config of the account app1.
app1:
edit: [mike]